Clear All
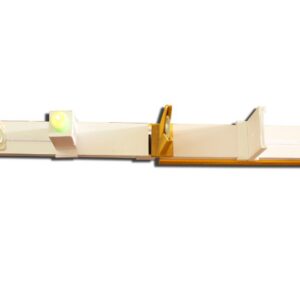
PAPER CHROMATOGRAPHY WORKING MODEL
Sale!6%
SCIENCE LAB EQUIPMENT WORKING MODEL / SCIENCE EXHIBITION WORKING MODEL
Original price was: ₹1,200.00.₹1,125.00Current price is: ₹1,125.00.
5 in stock
Description
Additional information
Reviews (0)
Q & A
PAPER CHROMATOGRAPHY WORKING MODEL
Paper chromatography is a method used in chemistry to separate and identify substances that are or can be dissolved in solvents. This technique is widely used for educational purposes as it is simple and demonstrates basic chromatographic principles. Here’s how you can perform paper chromatography using basic materials typically found in a school laboratory:
### What is Paper Chromatography?
Paper chromatography is a technique that involves placing a small dot or line of sample solution onto a strip of chromatography paper and then watching the components of the sample move up the paper with the solvent. It is used to separate the different components in a liquid mixture or identify potential substances within it.
### Materials Needed
– Chromatography paper or coffee filter paper
– A glass container
– A pencil (not a pen as pens contain inks that might run)
– Ruler
– Solvent (common solvents include water, alcohol, or acetone)
– Different colored water-soluble markers or inks
– A capillary tube or small brush for applying the ink
– A paper clip or string to hang the paper
### Steps to Perform Paper Chromatography
1. **Prepare the Paper:**
– Cut the chromatography paper into a long strip about 2 cm wide and 10 cm long.
– Draw a line with a pencil about 2 cm from the bottom of the strip. This is where you will apply your sample.
2. **Apply the Sample:**
– Use a capillary tube or a small brush to place a small dot of ink or marker at the center of the line.
– Allow the dot to dry completely, then reapply the ink several times to concentrate the sample, allowing each application to dry before reapplying.
3. **Set Up the Chromatography:**
– Fill the glass container with a small amount of solvent, just enough to cover the bottom.
– Attach the top of the paper strip to a pencil or stick using a paper clip.
– Place the pencil across the top of the container so the strip hangs down into it. The bottom of the paper should touch the solvent without the spot being submerged.
4. **Develop the Chromatogram:**
– As the solvent rises through the paper, it will dissolve the sample spot and carry it up the paper.
– Different components of the sample will move at different rates, causing them to separate along the paper strip.
5. **Remove and Dry:**
– Once the solvent has moved close to the top of the paper (or after a predetermined time), remove the paper from the container and hang it up to dry.
6. **Analyze the Results:**
– Measure the distance each component traveled from the original spot. Comparing these distances can help identify the substances present based on their “Rf values” (the ratio of the distance moved by the substance to the distance moved by the solvent).
### Learning Outcomes
Paper chromatography provides a visual demonstration of mixture separation, useful for teaching principles such as:
– **Solubility**: How soluble each component is in the chosen solvent.
– **Capillary Action**: How the solvent moves up the paper.
– **Component Migration**: How different substances are carried at different speeds by the solvent.
### Applications
This method is not only fundamental in educational experiments but also practical in fields like forensic science for analyzing the components of substances, environmental science for testing pollution levels, and anywhere else that simple, effective separation of compounds is necessary.
| Weight | 0.5 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 25 × 25 × 5 cm |
You must be logged in to post a review.
Q & A
Ask a question
There are no questions yet












Reviews
There are no reviews yet