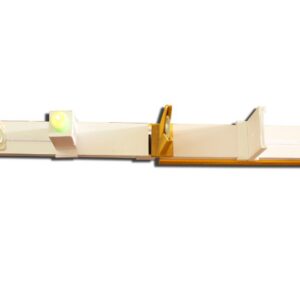
ELECTRIC CONDUCTIVITY OF ELECTROLITE WORKING MODEL
Sale!17%
SCIENCE LAB EQUIPMENT WORKING MODEL / SCIENCE EXHIBITION WORKING MODEL
Original price was: ₹1,500.00.₹1,250.00Current price is: ₹1,250.00.
5 in stock
Description
Additional information
Reviews (0)
Q & A
ELECTRIC CONDUCTIVITY OF ELECTROLITE
Electrolytes are substances that conduct electricity when dissolved in water or melted. They are composed of ions, which are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge.
When an electrolyte dissolves in water, it dissociates into ions, which are free to move and carry electric charge through the solution. This movement of ions is what allows electrolyte solutions to conduct electricity.
The conductivity of an electrolyte solution depends on several factors:
1. **Concentration**: The higher the concentration of ions in the solution, the greater the conductivity. This is because there are more ions available to carry electric charge.
2. **Nature of the ions**: The mobility of ions in solution depends on their size and charge. Smaller ions and ions with higher charge tend to move more easily through the solution, leading to higher conductivity.
3. **Temperature**: Generally, the conductivity of an electrolyte solution increases with temperature. This is because higher temperatures increase the mobility of ions, allowing them to move more freely through the solution.
4. **Type of electrolyte**: Different electrolytes have different conductivity properties. Strong electrolytes, which dissociate completely into ions in solution, have higher conductivity than weak electrolytes, which only partially dissociate.
Electrolyte solutions are commonly used in batteries, electroplating, electrolysis, and various chemical processes where the flow of electric charge is required. They play a crucial role in many aspects of chemistry, physics, and engineering.
Definition of Electrolytes:
- Electrolytes: Electrolytes are substances that dissociate into ions when dissolved in water or other solvents. These ions can be positively charged (cations) or negatively charged (anions).
- Types of Electrolytes:
- Strong Electrolytes: These substances completely dissociate into ions in solution. Examples include strong acids (e.g., HCl), strong bases (e.g., NaOH), and soluble salts (e.g., NaCl).
- Weak Electrolytes: These substances partially dissociate into ions in solution. Examples include weak acids (e.g., acetic acid) and weak bases (e.g., ammonia).
Electric Conductivity of Electrolytes:
- Ion Mobility:
- When an electrolyte is dissolved in water, it dissociates into positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions).
- These ions are free to move through the solution and carry electric charge.
- Electric Current Flow:
- When a potential difference (voltage) is applied across the electrolyte solution, the ions move towards oppositely charged electrodes.
- This movement of ions constitutes an electric current flowing through the solution.
- Conductivity Measurements:
- Electric conductivity of electrolytes is measured using a conductivity meter, which determines the ability of the solution to conduct electricity.
- Conductivity is usually reported in units of Siemens per meter (S/m) or microsiemens per centimeter (μS/cm).
- Factors Affecting Conductivity:
- Concentration of ions: Higher concentration of ions in the solution leads to higher conductivity.
- Temperature: Generally, conductivity increases with temperature due to greater ion mobility.
- Type of ions: The nature of the ions (size, charge, mobility) affects conductivity.
Applications of Electric Conductivity of Electrolytes:
- Chemical Analysis: Conductivity measurements are used in analytical chemistry for determining the concentration of ions in solutions.
- Industrial Processes: Monitoring and controlling the conductivity of electrolyte solutions is important in various industrial processes, such as electroplating, metal refining, and water treatment.
- Biological Systems: Understanding the conductivity of electrolyte solutions is essential in biological systems, such as the functioning of cells and tissues in the human body.
- Electrochemical Cells: Electrolyte solutions play a crucial role in electrochemical cells, including batteries, fuel cells, and electrolysis processes.
Conclusion:
Electric conductivity of electrolytes is a fundamental concept in chemistry and electrochemistry. It describes the ability of electrolyte solutions to conduct electricity, which is essential in various scientific, industrial, and biological applications. Understanding the factors affecting conductivity and measuring conductivity values helps in the analysis, control, and utilization of electrolyte solutions in diverse fields.
| Weight | 0.5 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 25 × 25 × 5 cm |
You must be logged in to post a review.
Q & A
Ask a question
There are no questions yet








Reviews
There are no reviews yet