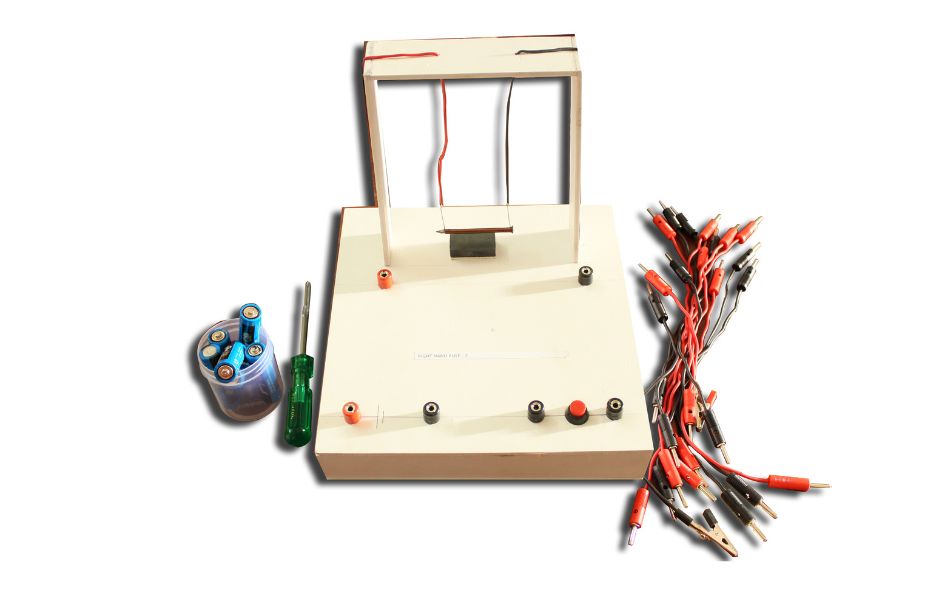
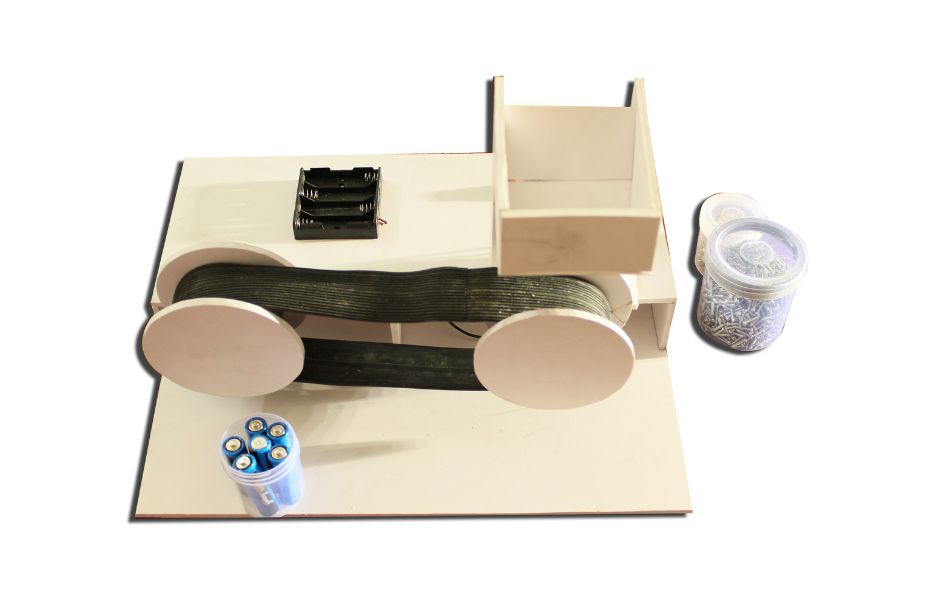
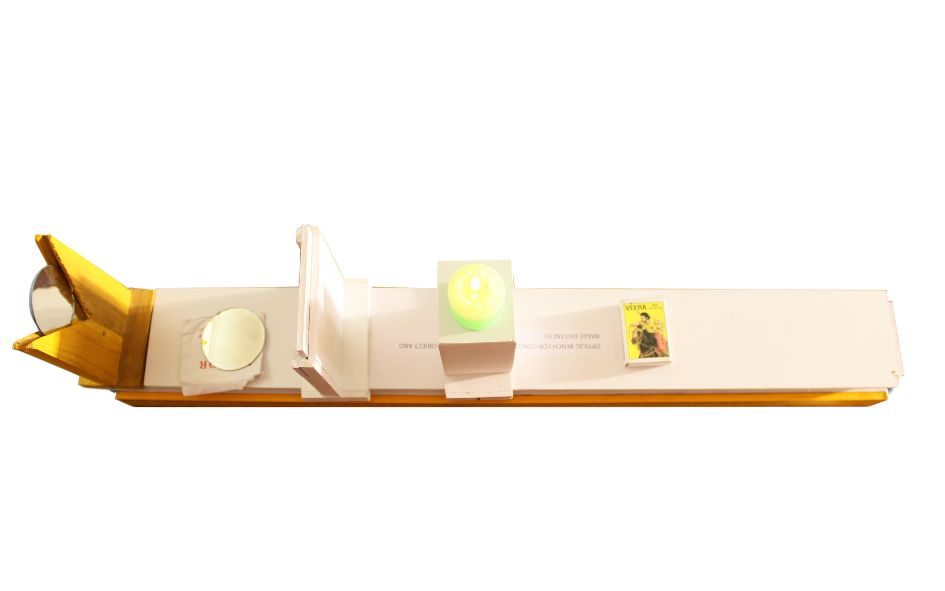
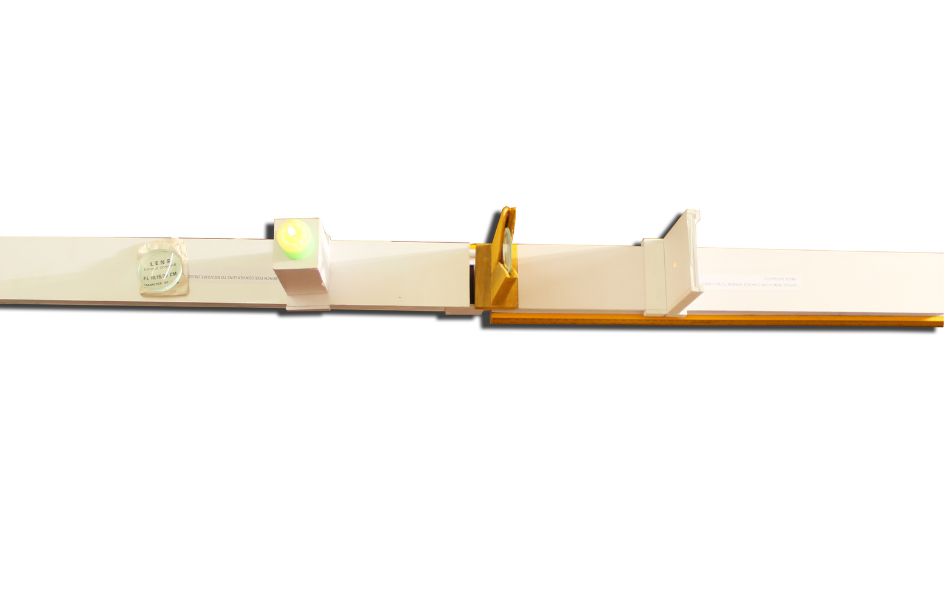
THE MOTION OF AN OBJECT MOVING IN A CIRCULAR PATH WORKING MODEL
SCIENCE LAB EQUIPMENT WORKING MODEL / SCIENCE EXHIBITION WORKING MODEL
4 in stock
Refund
Unfortunately, once an order is placed, there is no refund available. However, we do offer exchanges for defective or damaged items.
Due to the nature of our products and the potential for misuse or mishandling, we do not offer refunds. We believe in customer satisfaction and strive to provide quality exchanges for any issues that may arise.
If you have received a defective or damaged item, please contact our customer service team and they will assist you with the exchange process. Please note that exchanges are subject to availability and product conditions.
We do not offer refunds for change of mind purchases, but we do offer exchanges for valid reasons such as defects or damages.
Delivery
My Science Kart delivers orders through a reliable and efficient shipping service to ensure your products arrive safely and on time.
Yes, you can easily track your order from My Science Kart by using the tracking number provided to you once your order has been shipped.
If you have any issues with your order from My Science Kart, please contact our customer service team who will be happy to assist you and resolve any problems.
Payment
You can pay for your purchases on My Science Kart using various payment methods such as credit/debit cards, net banking, UPI’s and mobile wallets.
Yes, we use industry-standard encryption technology to protect your payment information and ensure that it is secure.
If you have any payment-related queries or issues on My Science Kart, you can contact our customer support team through the website or email us at support@mysciencekart.com.
THE MOTION OF AN OBJECT MOVING IN A CIRCULAR PATH
The motion of an object moving in a circular path is known as circular motion. This type of motion involves continuous change in direction, even if the object’s speed remains constant. Here are some key characteristics and concepts related to the motion of an object moving in a circular path:
**1. Constant Speed:**
– In circular motion, the object moves around the center of the circle at a constant speed. This means that the magnitude of the object’s velocity (speed) remains unchanged throughout the motion.
– Despite the constant speed, the direction of the object’s velocity vector is continuously changing, as it moves around the circle.
**2. Centripetal Acceleration:**
– Although the speed of the object remains constant, it experiences an acceleration called centripetal acceleration (\(a_c\)).
– Centripetal acceleration is directed towards the center of the circle and is responsible for continuously changing the object’s direction of motion while maintaining its speed.
– The magnitude of centripetal acceleration can be calculated using the formula:
[ a_c = v^2 / r ]
where \( v \) is the speed of the object and \( r \) is the radius of the circular path.
**3. Centripetal Force:**
– According to Newton’s second law of motion (\( F = ma \)), the centripetal acceleration of an object in circular motion requires a net force to act on it.
– This force, called the centripetal force, is directed towards the center of the circle and is responsible for maintaining the object’s motion along the circular path.
– The centripetal force can be provided by various mechanisms, such as tension in a string, gravitational attraction, or friction.
**4. Period and Frequency:**
– The time taken for the object to complete one full revolution around the circle is called the period (\( T \)) of the motion.
– The frequency (\( f \)) of the motion refers to the number of complete revolutions the object makes per unit time.
– The relationship between frequency and period is given by \( f = 1 / T ).
**Applications:**
– Circular motion is encountered in various real-life scenarios, such as the motion of planets around the sun, the motion of a car around a curved track, and the motion of a ceiling fan or a car wheel.
– Understanding circular motion is crucial in physics and engineering, as it provides insights into concepts such as velocity, acceleration, and force in rotational systems.
In summary, circular motion involves an object moving around a circular path with a constant speed, experiencing centripetal acceleration directed towards the center of the circle. The motion is characterized by continuous change in direction, even though the speed remains constant.
Characteristics of Circular Motion:
- Constant Speed:
- In circular motion, the object moves at a constant speed along the circular path. However, its velocity constantly changes due to the change in direction.
- Centripetal Force:
- Circular motion requires a centripetal force directed towards the center of the circle. This force is necessary to keep the object moving in a circular path instead of flying off tangentially.
- The centripetal force can be provided by various factors, such as tension in a string, gravitational attraction, friction, or a magnetic force.
- Acceleration:
- Although the object’s speed remains constant, it experiences centripetal acceleration directed towards the center of the circle.
- Centripetal acceleration is perpendicular to the velocity vector and causes the object to change direction continuously.
- Angular Velocity:
- Angular velocity measures the rate of rotation or angular displacement of the object around the center of the circle.
- It is defined as the angle swept out per unit time and is usually measured in radians per second.
Examples of Circular Motion:
- Planetary Orbits:
- Planets and satellites in the solar system move in nearly circular orbits around the Sun or their parent bodies due to gravitational forces.
- The centripetal force in this case is provided by the gravitational attraction between the celestial bodies.
- Motion of a Carousel:
- A carousel or merry-go-round at an amusement park provides a classic example of circular motion.
- Riders on the carousel experience centripetal acceleration as they move around the circular path.
- Whirling a Yo-Yo:
- When a yo-yo is whirled around in a circular motion at the end of a string, it experiences circular motion.
- The tension in the string provides the centripetal force necessary to keep the yo-yo moving in a circular path.
Conclusion:
Circular motion involves the movement of an object along a circular path with a constant speed. It requires a centripetal force directed towards the center of the circle to maintain the object’s motion. Understanding circular motion is essential in various fields, including physics, engineering, and astronomy, as it plays a significant role in describing the motion of objects in our everyday lives and the universe.
| Weight | 0.5 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 25 × 25 × 5 cm |
You must be logged in to post a review.
Q & A
Related Products
BASIC ELECTRIC CIRCUIT ( THREE CASES) WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
REFRACTIVE INDEX OF THE PRISAM WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
SEPARATING IRON FROM THE SOIL WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
REFLECTION OF LIGHT PLANE MIRRORS/LAWS OF REFLECTION WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
AC MOTOR WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
OERSTED EXPERIMENT WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
KIRCHHOFF'S JUNCTION LAW WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
ELECTRIC SHOCK WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
Product categories
- Circuits & Projects 233
- My Science Kart 665
- Raw Materials For Projects & Lab Equipments 381
- Science Exhibition 516
- Science Exhibition Projects & Working Models 344
- Biology Science Exhibition Projects & Working Models 31
- Chemistry Science Exhibition Projects & Working Models 12
- Mathematics Science Exhibition projects & Working Models 7
- Physics Science Exhibition Projects & Working Models 129
- Robotics Science Exhibition Projects & Working Models 23
- Social Science Exhibition Projects & Working Models 20
- Science Lab Equipments With Working Models 363
Cart
TRULY INDIAN EDUCATION BRAND
Over 10,000+ Happy Customers
My Science Kart
Address:- Ground floor, Lakshmi Nagar, D.No:- 40-1/1-5, PVP Mall Backside, Mogalrajapuram, Labbipet, Vijayawada, Andhra Pradesh 520010
7673977997, 0866-3543677
mysciencekart@gmail.com
Categories
MAP
© My Science Kart 2024, Designed & Developed By Synfocy Tech Solutions



















Reviews
There are no reviews yet