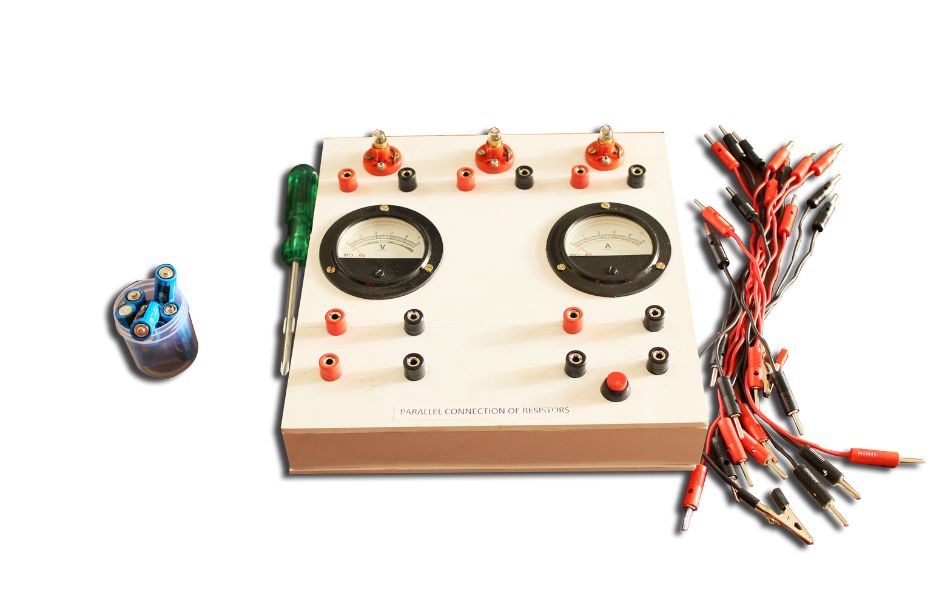
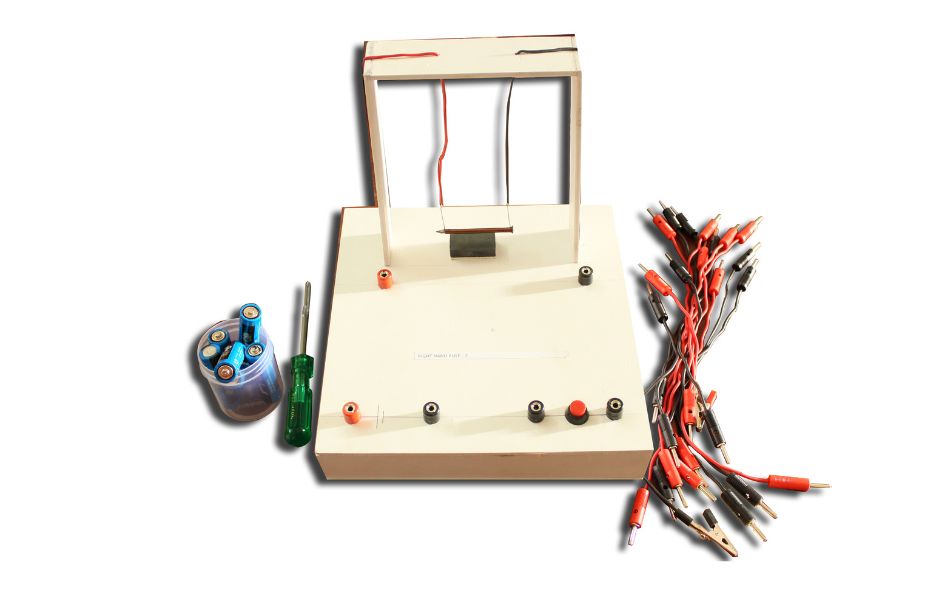
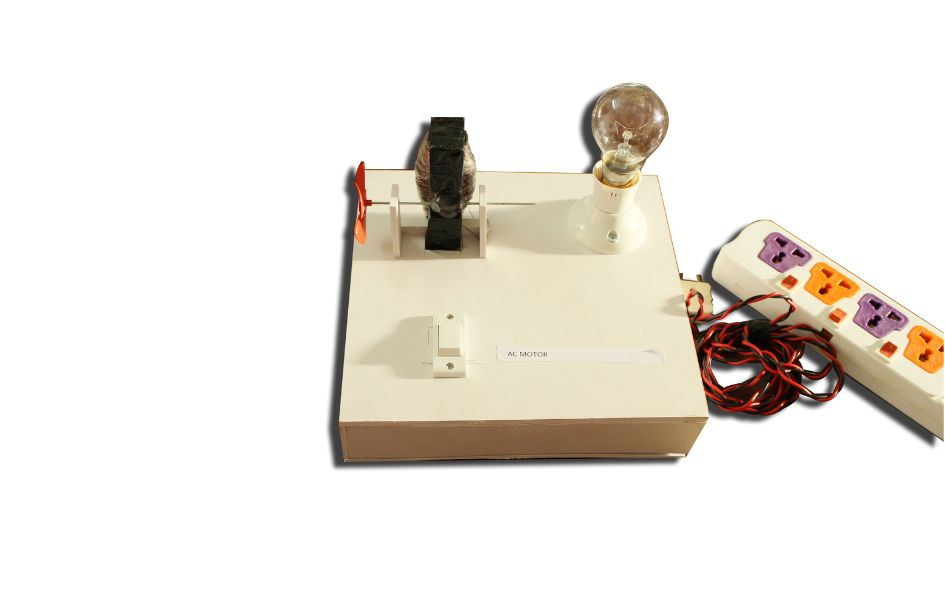
SIMPLE ELECTRIC CIRCUIT WORKING MODEL
SCIENCE LAB EQUIPMENT WORKING MODEL / SCIENCE EXHIBITION WORKING MODEL
5 in stock
Refund
Unfortunately, once an order is placed, there is no refund available. However, we do offer exchanges for defective or damaged items.
Due to the nature of our products and the potential for misuse or mishandling, we do not offer refunds. We believe in customer satisfaction and strive to provide quality exchanges for any issues that may arise.
If you have received a defective or damaged item, please contact our customer service team and they will assist you with the exchange process. Please note that exchanges are subject to availability and product conditions.
We do not offer refunds for change of mind purchases, but we do offer exchanges for valid reasons such as defects or damages.
Delivery
My Science Kart delivers orders through a reliable and efficient shipping service to ensure your products arrive safely and on time.
Yes, you can easily track your order from My Science Kart by using the tracking number provided to you once your order has been shipped.
If you have any issues with your order from My Science Kart, please contact our customer service team who will be happy to assist you and resolve any problems.
Payment
You can pay for your purchases on My Science Kart using various payment methods such as credit/debit cards, net banking, UPI’s and mobile wallets.
Yes, we use industry-standard encryption technology to protect your payment information and ensure that it is secure.
If you have any payment-related queries or issues on My Science Kart, you can contact our customer support team through the website or email us at support@mysciencekart.com.
SIMPLE ELECTRIC CIRCUIT
Creating a simple electric circuit is a great way to understand the basic principles of electricity and circuitry. Here’s how you can make a simple circuit using a battery, a light bulb, and some wires:
**Materials Needed:**
1. Battery (AA, AAA, or any other low-voltage battery)
2. Light bulb (preferably a small LED bulb for safety)
3. Holder for the light bulb (socket or clip)
4. Wires with alligator clips or stripped ends
5. Optional: Switch for controlling the circuit
**Procedure:**
1. **Safety Precautions:**
– Ensure the battery voltage matches the voltage rating of the light bulb. For example, if you’re using a 1.5V battery, use a 1.5V LED bulb.
– Use caution when handling batteries, especially when connecting them in a circuit. Ensure the polarity (+ and -) of the battery and bulb are matched correctly to avoid short circuits.
2. **Connecting the Circuit:**
– Connect one end of the wire to the positive terminal (+) of the battery.
– Connect the other end of the wire to one terminal of the light bulb holder.
– Connect another wire from the negative terminal (-) of the battery to the other terminal of the light bulb holder.
– Ensure the connections are secure and there are no loose wires or exposed metal.
3. **Testing the Circuit:**
– Once the circuit is connected, the light bulb should light up if the connections are correct and the battery has enough power.
– If the light bulb doesn’t light up, double-check the connections, and ensure the battery is fully charged or replace it with a new one.
4. **Optional: Adding a Switch:**
– To control the flow of electricity in the circuit, you can add a switch between one of the wires connecting the battery and the light bulb.
– Connect one end of the switch to one of the wires between the battery and the light bulb holder.
– Connect the other end of the switch to the remaining wire to complete the circuit.
– When the switch is closed (turned on), the circuit is complete, and the light bulb will light up. When the switch is open (turned off), the circuit is broken, and the light bulb will turn off.
By following these steps, you can create a simple electric circuit and gain a better understanding of how electricity flows in a closed loop to power devices like light bulbs.
Components of a Simple Electric Circuit
- Power Source: Typically a battery or generator. It provides the necessary electric potential (voltage) that drives the electric current through the circuit.
- Conductor (Wires): Conductive material (usually copper or aluminum) that forms a path for the current to flow. These wires connect the components of the circuit.
- Load (e.g., Light Bulb): The component that uses the electricity to perform work, such as lighting a bulb, turning a motor, or heating an element.
- Switch (optional): A component used to open or close the circuit. When the switch is open, no current flows; when it’s closed, current flows through the circuit.
- Connecting Elements (such as terminals and connectors): These ensure that the components are properly connected so that electricity flows efficiently.
How It Works
Step-by-Step Process:
- Starting the Circuit:
- When the circuit is complete (i.e., closed), the power source such as a battery provides a voltage (electric potential difference) across the two ends of the circuit.
- Flow of Electrons:
- The voltage from the power source exerts a force on the free electrons in the conductor (wires). These electrons start moving along the wire towards the positive terminal of the battery, creating an electric current.
- Current Through the Load:
- The electric current flows through the circuit passing through any loads present, such as a light bulb. Inside the bulb, the current flows through the filament (usually made of tungsten), which has a relatively high resistance.
- As the electrons move through the filament, their kinetic energy is transferred to the atoms of the tungsten filament, causing it to heat up and emit light.
- Completing the Circuit:
- After passing through the load, the electrons continue through the circuit, returning to the negative terminal of the battery.
- This continuous flow of electrons keeps the bulb lit as long as the circuit remains closed and the battery provides voltage.
Role of Each Component:
- Battery: It pushes the electrons through the circuit by providing the necessary voltage.
- Wires: Serve as the pathway for the electrons to move through the circuit.
- Light Bulb: Uses the energy carried by the electrons to produce light and heat.
- Switch: Allows control over the flow of electricity; can stop the flow (turn off the light) or allow it (turn on the light).
Closing Thoughts
The basic operation of a simple electric circuit involves the flow of electrons driven by a voltage source through a conductive path and doing work at the load before returning to the source. Understanding this process is crucial for grasping more complex electrical and electronic systems. In practical applications, knowing how to manipulate the flow of electricity with components such as switches and understanding the role of resistors (not discussed in detail here but often present to manage the flow and distribution of current) is essential for building, troubleshooting, and improving electrical systems.
| Weight | 0.5 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 25 × 25 × 5 cm |
You must be logged in to post a review.
Q & A
Related Products
RIGHT HAND RULE - 1 WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
HEAT, TEMPERATURE and KINETIC ENERGY WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
MAGNETIC FIELD DUE TO STRAIGHT WIRE CARRYING CURRENT WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
LIGHT RAY TRAVELS FROM A DENSER MEDIUM TO RARER MEDIUM WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
OPTICAL BENCH FOR CONCAVE MIRROR /or OPTICAL BENCH FOR MEASURING OBJECT AND IMAGE DISTANCE BY USING CONCAVE MIRROR WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
OHM'S LAW WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
RIGHT HAND RULE - 2 WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
THE RELATION BETWEEN ANGLE OF INCIDENCE AND AND ANGLE OF REFRACTION WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
Product categories
- Circuits & Projects 233
- My Science Kart 665
- Raw Materials For Projects & Lab Equipments 381
- Science Exhibition 516
- Science Exhibition Projects & Working Models 344
- Biology Science Exhibition Projects & Working Models 31
- Chemistry Science Exhibition Projects & Working Models 12
- Mathematics Science Exhibition projects & Working Models 7
- Physics Science Exhibition Projects & Working Models 129
- Robotics Science Exhibition Projects & Working Models 23
- Social Science Exhibition Projects & Working Models 20
- Science Lab Equipments With Working Models 363
Cart
TRULY INDIAN EDUCATION BRAND
Over 10,000+ Happy Customers
My Science Kart
Address:- Ground floor, Lakshmi Nagar, D.No:- 40-1/1-5, PVP Mall Backside, Mogalrajapuram, Labbipet, Vijayawada, Andhra Pradesh 520010
7673977997, 0866-3543677
mysciencekart@gmail.com
Categories
MAP
© My Science Kart 2024, Designed & Developed By Synfocy Tech Solutions




























Reviews
There are no reviews yet