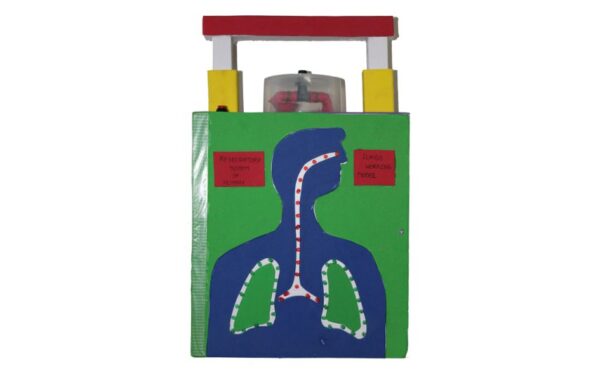

LUNGS WORKING MODEL
SCIENCE LAB EQUIPMENT WORKING MODEL / SCIENCE EXHIBITION WORKING MODEL / BIOLOGY WORKING MODEL
3 in stock
Refund
Unfortunately, once an order is placed, there is no refund available. However, we do offer exchanges for defective or damaged items.
Due to the nature of our products and the potential for misuse or mishandling, we do not offer refunds. We believe in customer satisfaction and strive to provide quality exchanges for any issues that may arise.
If you have received a defective or damaged item, please contact our customer service team and they will assist you with the exchange process. Please note that exchanges are subject to availability and product conditions.
We do not offer refunds for change of mind purchases, but we do offer exchanges for valid reasons such as defects or damages.
Delivery
My Science Kart delivers orders through a reliable and efficient shipping service to ensure your products arrive safely and on time.
Yes, you can easily track your order from My Science Kart by using the tracking number provided to you once your order has been shipped.
If you have any issues with your order from My Science Kart, please contact our customer service team who will be happy to assist you and resolve any problems.
Payment
You can pay for your purchases on My Science Kart using various payment methods such as credit/debit cards, net banking, UPI’s and mobile wallets.
Yes, we use industry-standard encryption technology to protect your payment information and ensure that it is secure.
If you have any payment-related queries or issues on My Science Kart, you can contact our customer support team through the website or email us at support@mysciencekart.com.
LUNGS WORKING MODEL |
The human lungs are vital organs responsible for the exchange of gases, primarily oxygen and carbon dioxide, between the body and the environment. Here’s how the human lungs work:
**1. Breathing Process:**
– Breathing begins with the inhalation of air through the nose or mouth. The air travels through the respiratory tract and enters the lungs through the trachea (windpipe).
– The trachea branches into two bronchi, each leading to one lung. Inside the lungs, the bronchi further divide into smaller tubes called bronchioles.
– At the end of the bronchioles are clusters of tiny air sacs called alveoli, where gas exchange occurs.
**2. Gas Exchange:**
– In the alveoli, oxygen from the inhaled air diffuses across the thin walls of the alveoli and into the surrounding capillaries (tiny blood vessels).
– Oxygen binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells, forming oxyhemoglobin. Oxygen-rich blood is then transported to body tissues through the bloodstream.
– At the same time, carbon dioxide, a waste product of cellular metabolism, diffuses from the blood in the capillaries into the alveoli.
– Carbon dioxide is exhaled from the lungs during exhalation, completing the process of gas exchange.
**3. Lung Function:**
– The lungs are enclosed within the thoracic cavity, protected by the rib cage and supported by the diaphragm, a dome-shaped muscle located below the lungs.
– During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and moves downward, increasing the volume of the thoracic cavity. This creates negative pressure within the lungs, causing air to rush in and fill the expanded space.
– During exhalation, the diaphragm relaxes and moves upward, decreasing the volume of the thoracic cavity. This creates positive pressure within the lungs, causing air to be expelled from the lungs.
**4. Regulation of Breathing:**
– Breathing is controlled by the respiratory center located in the brainstem. It receives input from sensors that monitor oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood, as well as pH levels.
– The respiratory center adjusts the rate and depth of breathing to maintain optimal levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood.
**Key Points:**
– The main function of the lungs is to facilitate the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the body and the environment.
– Gas exchange occurs in the alveoli, where oxygen enters the bloodstream and carbon dioxide exits the bloodstream.
– Breathing is controlled by the respiratory center in the brainstem, which regulates the rate and depth of breathing to maintain homeostasis.
In summary, the human lungs play a crucial role in the respiratory system by enabling the exchange of gases necessary for cellular function and overall health.
Detailed Article on “LUNGS WORKING”
I. Introduction Lungs are pivotal in the respiratory system, serving as the primary site for gas exchange in the body. Understanding how lungs work is crucial for grasping the essentials of human physiology and health.
II. Anatomy of the Lungs The lungs are composed of several critical components, each playing a unique role in breathing. The lobes and segments tailor the lungs’ shape and function, while the airways, extending from the trachea to the microscopic alveoli, facilitate air movement.
A. The Pleura: Roles and Functions Surrounding the lungs, the pleura comprises two thin layers of cells providing vital lubrication and protection against the rib cage during breathing.
III. The Process of Breathing Breathing involves two main processes: inhalation and exhalation. The diaphragm contracts during inhalation, increasing thoracic volume and reducing pressure to draw air in. Exhalation relies on the elastic recoil of lung tissues and the relaxation of respiratory muscles.
IV. Gas Exchange Mechanism At the alveolar level, oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse passively across cell membranes, a critical process facilitated by the immense surface area of the lungs and their close association with the bloodstream.
V. Lung Health and Maintenance Lung health is threatened by diseases such as asthma and COPD. Preventive strategies are crucial, including smoking cessation and minimizing exposure to pollutants.
VI. Impact of Environment on Lung Function Environmental factors such as poor air quality and high altitudes can severely affect lung function, illustrating the need for robust public health policies.
VII. The Role of Lungs in the Body’s Overall Health The lungs interact with nearly every system in the body, highlighting their
| Weight | 1 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 50 × 40 × 6 cm |
You must be logged in to post a review.
Q & A
Related Products
MAGNETIC FIELD DUE TO SOLENOID WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
OERSTED EXPERIMENT WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
REFRACTIVE INDEX OF THE PRISAM WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
THE RELATION BETWEEN ANGLE OF INCIDENCE AND AND ANGLE OF REFRACTION WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
LIGHT RAY TRAVELS FROM A DENSER MEDIUM TO RARER MEDIUM WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
a. NATURE OF MATERIAL AND RESISTANCE b. LENGTH OF CONDUCTOR AND RESISTANCE c. CROSS SECTION AREA AND RESISTANCE WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
HEAT, TEMPERATURE and KINETIC ENERGY WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
SEPARATING IRON FROM THE SOIL WORKING MODEL
- ✓ 100% Quality products
Product categories
- Circuits & Projects 233
- My Science Kart 665
- Raw Materials For Projects & Lab Equipments 381
- Science Exhibition 516
- Science Exhibition Projects & Working Models 344
- Biology Science Exhibition Projects & Working Models 31
- Chemistry Science Exhibition Projects & Working Models 12
- Mathematics Science Exhibition projects & Working Models 7
- Physics Science Exhibition Projects & Working Models 129
- Robotics Science Exhibition Projects & Working Models 23
- Social Science Exhibition Projects & Working Models 20
- Science Lab Equipments With Working Models 363
Cart
TRULY INDIAN EDUCATION BRAND
Over 10,000+ Happy Customers
My Science Kart
Address:- Ground floor, Lakshmi Nagar, D.No:- 40-1/1-5, PVP Mall Backside, Mogalrajapuram, Labbipet, Vijayawada, Andhra Pradesh 520010
7673977997, 0866-3543677
mysciencekart@gmail.com
Categories
MAP
© My Science Kart 2024, Designed & Developed By Synfocy Tech Solutions





















Reviews
There are no reviews yet